Macronutrient Content of a Big Mac Meal
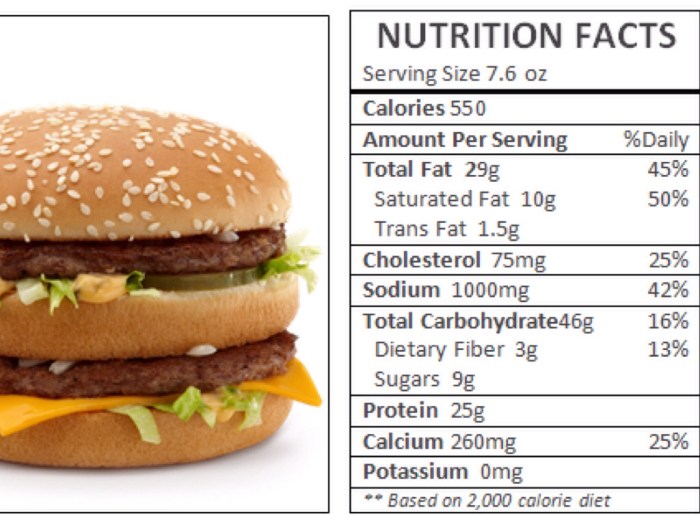
Big mac meal nutrition facts – A Big Mac meal, typically consisting of a Big Mac sandwich, medium fries, and a medium Coca-Cola, provides a substantial amount of calories and macronutrients. Understanding its macronutrient composition is crucial for assessing its nutritional value and impact on one’s daily dietary intake. This section details the macronutrient breakdown of a standard Big Mac meal and compares it to general daily recommendations.
Macronutrient Breakdown of a Big Mac Meal
The exact macronutrient content can vary slightly depending on location and preparation, but a typical Big Mac meal contains approximately: 50-70 grams of fat, 150-200 grams of carbohydrates, and 40-50 grams of protein. These figures represent a significant portion of the recommended daily intake for many individuals, underscoring the meal’s high caloric density.
Understanding the nutritional content of a Big Mac meal is crucial for mindful eating. For comparison, you might want to check out the nutritional information for other popular fast-food chains, such as the details provided at in and out burger nutrition facts , to see how different menu items stack up. Returning to the Big Mac, its high calorie and fat content should be considered alongside individual dietary needs and goals.
Comparison to Recommended Daily Intake
The recommended daily intake of macronutrients varies based on factors such as age, sex, activity level, and overall health goals. However, general guidelines suggest that a balanced diet includes a moderate amount of fat, a sufficient amount of carbohydrates for energy, and adequate protein for building and repairing tissues. A Big Mac meal’s high fat and carbohydrate content often surpasses the recommended daily percentages for these macronutrients, particularly in a single meal.
The protein content, while substantial, might not entirely meet the daily requirement for many individuals depending on their needs. It’s important to note that these comparisons are general estimates, and individual dietary needs vary considerably.
Sources of Macronutrients in a Big Mac Meal, Big mac meal nutrition facts
- Fat: The majority of fat comes from the Big Mac’s beef patty, cheese, mayonnaise-based special sauce, and the frying oil used for the potatoes. These sources contribute to the meal’s high saturated and trans fat content.
- Carbohydrates: The primary carbohydrate sources are the Big Mac buns, the fried potatoes, and the sugar in the Coca-Cola. These contribute significantly to the meal’s overall carbohydrate count and sugar content.
- Protein: The beef patty is the main source of protein in the Big Mac meal, while smaller amounts are also found in the cheese and buns. While protein is essential, the type and quality of protein within the meal should also be considered.
Sodium and Sugar Content in a Big Mac Meal

A Big Mac meal, encompassing the burger, fries, and a soft drink, represents a significant intake of sodium and sugar, far exceeding recommended daily allowances for many individuals. Understanding these levels is crucial for making informed dietary choices.The exact amounts vary slightly depending on the specific restaurant and size of the drink, but a typical Big Mac meal contains approximately 1,000-1,200 mg of sodium and 70-90 grams of sugar.
This represents a substantial portion of the recommended daily intake of both nutrients. The American Heart Association recommends a maximum of 2,300 mg of sodium per day, while the World Health Organization suggests limiting added sugars to less than 10% of total daily calories. For an average adult, this translates to roughly 25 grams of added sugar.
Sodium Content Comparison with Other Fast-Food Meals
A Big Mac meal’s sodium content is relatively high compared to other fast-food options. While many fast-food meals contain significant sodium, a Big Mac meal frequently surpasses the sodium levels found in comparable meals from other chains. For instance, a similar meal from a competing fast-food restaurant might contain 800-900mg of sodium, showcasing the higher sodium content in a Big Mac meal.
This difference stems from the ingredients used in the burger, the seasoning of the fries, and the sodium content of the accompanying soft drink.
Sugar Content Comparison with Other Fast-Food Meals
The sugar content in a Big Mac meal is also considerably high. The primary source of sugar is the soft drink, which often contains significant amounts of high-fructose corn syrup. While other fast-food meals might also include sugary drinks, the combination of the drink with the relatively high sugar content in the bun and sauces in a Big Mac meal contributes to a higher overall sugar level.
A comparable meal from another chain, even with a sugary drink, might contain 50-60 grams of sugar, still less than a Big Mac meal.
Potential Health Implications of High Sodium and Sugar Intake
Consuming high levels of sodium and sugar on a regular basis can contribute to various health problems. High sodium intake is linked to increased blood pressure, a major risk factor for heart disease and stroke. Excessive sugar consumption can lead to weight gain, type 2 diabetes, and other metabolic disorders. Regular consumption of a Big Mac meal, with its high sodium and sugar content, significantly increases the risk of developing these conditions over time.
For example, consistent consumption of meals with this high sodium content can elevate blood pressure gradually, increasing the risk of cardiovascular complications later in life. Similarly, consistent high sugar intake can contribute to insulin resistance and the development of type 2 diabetes. The cumulative effect of frequent consumption of such meals significantly increases health risks.
Top FAQs: Big Mac Meal Nutrition Facts
What are the potential long-term health effects of regularly consuming Big Mac meals?
Regular consumption of high-calorie, high-fat, high-sodium meals like the Big Mac meal can increase the risk of weight gain, obesity, heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and other chronic health problems.
Are there any vegetarian or vegan alternatives to the Big Mac meal?
Many fast-food chains now offer vegetarian and vegan options, such as veggie burgers, salads, or plant-based alternatives to traditional meat dishes. It’s advisable to check the specific menu and nutritional information of your chosen restaurant.
How does the nutritional content of a Big Mac meal vary across different countries?
Nutritional content can vary slightly depending on local ingredients and recipes. However, the overall nutritional profile remains generally consistent across most locations.
Can I modify a Big Mac meal to make it healthier?
Yes, you can request modifications such as removing certain ingredients (e.g., cheese, special sauce), choosing a smaller portion of fries, or opting for a healthier beverage like water or unsweetened tea.






